This article is part of the This Week in PowerBites Library Series.
Li-Ion Without Tears (or Fires!)
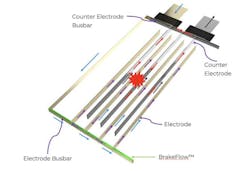
Enovix Corp. released a white paper that provides some insights about how its next-generation 3D silicon lithium-ion (Li-ion) battery architecture is able to dramatically increase power density and longevity without compromising safety. The paper, titled “Enovix BrakeFlow Technology,” describes the company’s intra-cell connection system that protects the battery against thermal runaway from internal short circuits, without compromising high energy density.
As described in Electronic Design's recent feature on advanced battery technologies, the Enovix battery architecture is based on an array of cells that are horizontally stacked within a laser-cut frame, used to constrain the expansion and resulting mechanical strain their silicon electrodes generate during each charge/discharge cycle.
The paper provides additional details about how the 3D cell is divided into many sub-cell units, each having a discrete connection to a laser-cut common anode or cathode busbar. These sub-cells are in turn connected through Enovix's BrakeFlow system that’s engineered—based on the number of electrodes and the individual electrode’s area—to limit the discharge current from the remainder of the cell, through the shorted sub-unit.
You can download Enovix's BrakeFlow white paper by clicking here. Additional details can be seen in the video below, featuring Enovix Chairman TJ Rodgers explaining thermal runaway and how its unique architecture prevents it:
Cool-Running 950-V MOSFETs with Fast Integrated Body Diode Target Industrial, Lighting Apps
A new 950-V MOSFET family developed by Infineon Technologies is based on its PFD7 high-voltage superjunction (SJ) technology that provides high performance and simplified design requirements. In addition, the devices integrate a fast body diode that ensures robust performance and a reduced bill of materials (BOM) for applications where high efficiency and reliability are essential, including lighting systems, as well as consumer and industrial SMPS applications.
The new devices incorporate features that enable robust, reliable commutation for flyback, power-factor-correction (PFC), and LLC/LCC designs, including half- or full-bridge configurations. By integrating an ultra-fast body diode with ultra-low reverse-recovery charge (Qrr), they offer hard commutation ruggedness and reliability. A gate-source threshold voltage (V(GS),th) of 3 V and smallest V(GS),th variation of ±0.5 V makes the new devices easy to design-in and drive, leading to increased design freedom.
Due to the low threshold voltage and tolerance, MOSFET linear mode operation is avoided while lowering driving voltage and reducing idle loss. The reduced losses can improve the new MOSFETs' light- and full-load PFC efficiency by more than 0.2% while matching the performance with regards to LLC efficiency.
The devices’ significantly reduced switching losses (EOSS, QOSS, and Qg) improve efficiency in hard- and soft-switching applications and result in up to 4°K lower MOSFET temperature compared to 900-V CoolMOS C3 SJ MOSFETs. The new MOSFETs also offer up to 55% lower on-resistance (RDS(on)) devices in various SMD and THD packages, such as 450 mΩ in DPAK or 60 mΩ in TO-247 packages. This enables designers to use smaller packages and boost power density and board space savings at reduced BOM and production costs.
All product variants of Infineon's 950-V CoolMOS PFD7 family can be ordered now. Additional information is available at www.infineon.com/pfd7-950v.
ZVS Power-Supply ICs Offer Programmability, High Efficiency, and Small Form Factor
Implementing the latest members of Power Integrations' InnoSwitch4-Pro family of flyback switching-supply controllers, designers can create compact power adapters that support the USB PD and Universal Fast Charging specifications while delivering up to 220 W at over 95% efficiency.
The digitally controllable, offline CV/CC zero-voltage-switching (ZVS) flyback ICs combine a 750-V PowiGaN primary switch, controller, FluxLink reinforced isolation feedback link for secondary-side control, I2C interface, active clamp drive, and synchronous rectification in a compact InSOP-28 package. Such a high level of integration greatly simplifies the development and manufacture of fully programmable, efficient power supplies for cellphone, notebook, tablet, and multi-port accessories.
InnoSwitch4-Pro ICs leverage a unique control algorithm that supports ZVS during both discontinuous conduction mode (DCM) and continuous conduction mode (CCM) at steady-state switching frequencies of up to 140 kHz. When paired with the ClampZero IC, the algorithm allows for higher-frequency operation without a corresponding drop in efficiency.
The controllers also support quasi-resonant switching in DCM and CCM when used as a standalone product. DCM-only operation can be selected to reduce SR FET voltage stress. In addition, an optimized command set reduces I2C traffic.
InnoSwitch4-Pro flyback switcher ICs provide exceptional CV/CC accuracy, independent of external components, and consume less than 30 mW no-load while offering line-sensing and comprehensive protection features. Devices are fully protected, featuring auto-restart or latching fault response for output overvoltage and undervoltage protection, multiple output undervoltage fault thresholds, latching or hysteretic primary overtemperature protection, and output bus switch short-circuit protection.
These programmable flyback ICs in combination with ClampZero and MinE-CAP companion devices reduce input capacitor size requirements over an equivalent conventional design by roughly 40%. Meanwhile, thanks to the controller's operating efficiency, typically in excess of 95%, designers can achieve even higher power densities by eliminating the heatsinks, spreaders, and potting materials typically required for thermal management.
Availability & Resources
Two reference designs, the DER-960 (100 W) and RDK-942 (65 W), are available for designers wishing to evaluate the InnoSwitch4-Pro IC. Devices are priced at $1.85 for 10,000-unit quantities. For further information, contact a Power Integrations sales representative or one of the company’s authorized worldwide distributors: Digi-Key, Farnell, Mouser and RS Components, or visit power.com.
MOSFETs Offer Top-Cooled Packages for Compact, Cooler-Running Automotive Apps
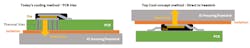
A series of new MOSFET devices from onsemi feature top-side cooling to assist designers in challenging automotive applications, especially within motor control and dc-dc conversion. Housed in a TCPAK57 package measuring just 5 × 7 mm, the new Top Cool devices feature a 16.5-mm2 thermal pad on the top side. This allows heat to be dissipated directly into a heatsink rather than via a typical printed circuit board (PCB).
By enabling the use of both sides of the PCB and decreasing the amount of heat going into it, the TCPAK57 boosts power density. Improved reliability of the new design adds to an overall extended system lifetime.
The initial TCPAK57 portfolio includes 40-, 60-, and 80-V devices that can deliver the electrical efficiency required in high-power applications with RDS(on) values as low as 1 mΩ. In addition, the gate charge (Qg) is low (65 nC), reducing losses in high-speed switching applications.
All devices will operate at junction temperatures (Tj) of 175°C and are AEC-Q101-qualified and PPAP-capable. This, along with their gull wings that allows for inspection of solder joints and superior board-level reliability, makes them well-suited for demanding automotive applications. The target applications are high/medium power motor controls such as electric power steering and oil pumps.
Samples of the new devices are available now, with full-scale manufacture planned in January 2023. Additional information about onsemi's new single N-channel power MOSFETs can be found on the company's website.
Small, Flexible Synchronous Buck Controller Handles Extreme Step-Down Ratios
With compact dimensions and an input-voltage range from 6 to 75 V, STMicroelectronics’ L3751 synchronous buck controller serves a wide range of applications, including industrial equipment and battery-powered light electric vehicles. The 3.5- × 4.5-mm controller also is well-suited for use in telecom and networking equipment that feature commonly used 24- and 48-V buses.
With a minimum on-time duration of 40 ns, the L3751 can support an extremely low duty cycle thereby permitting a large step-down ratio. As a result, it can power low-voltage devices directly without intermediate conversion, which helps simplify circuit design and lower BOM costs. The device's integrated 7.5-V supply eliminates the need for discrete gate drivers.
In addition to having a wide supply-voltage range, the L3751 has 100-V-tolerant inputs that allow for operation in harsh electrical environments. The switching frequency is adjustable from 100 kHz to 1 MHz, giving designers flexibility to optimize circuit size, performance, and cost through selection of the external MOSFETs and passive components. To enhance efficiency and minimize ripple, the L3751 operates in diode-emulation mode and with pulse skipping at light loads.
Protection functions include thermal protection, input undervoltage lockout, constant-current protection with hiccup mode, and programmable current sensing. There’s also an external Enable pin and open-collector power-good indicator.
The L3751 is in production now and available in a QFN20 package with wettable flanks that aid inspection. It’s priced from $1.36 for orders of 1,000 pieces. Designers can accelerate the device selection process for their power-supply development efforts with the STEVAL-L3751V12 100-W evaluation board, which is available now.
Enhanced Fast Recovery Diodes Deliver Low-Loss Performance and Ultra-Low-Noise Characteristics
ROHM Semiconductor's RFL/RFS series of advanced 650-V fast recovery diodes (FRDs) provide the low forward voltage (VF), fast reverse-recovery time (trr), and ultra-low noise characteristics required to support high-power industrial and consumer equipment, such as air conditioners and EV charging stations.
The FRDs were developed to address the need for greater energy efficiency arising from the electrification of the global economy. The upcoming generation of white goods and industrial equipment require not only high electrical efficiency, but also cleaner loads that reduce the cost and complexity of the countermeasures needed to meet global standards for noise and power factor correction.
The new RFL/RFS series uses an optimized device structure and materials that allows them to achieve the optimum balance between VF and trr for specific applications. The RFL series reduces VF by approximately 3.2% and trr by about 8.3% over the conventional RFN series, while the high-speed RFS series decreases VF by approximately 17.9% versus the conventional RFUH series. Both products contribute to higher power-supply efficiency through optimal design based on circuit requirements.
Applications include:
- Power-factor-correction circuits in air conditioners, washers, refrigerators, etc.
- Secondary rectifier circuits in EV charging stations, etc.
- Inverter circuits in machine tool robots, compressors, etc.
- Power supplies for servers, base stations, and more
Topology Selection
When designing power-supply circuits, it’s necessary to select a circuit configuration (topology) that matches the specific requirements (input/output voltages, power, isolation, etc.) of a particular application. To simplify the process, ROHM offers a component selection page that recommends the optimum products for many of the most widely used circuit topologies.
ROHM's advanced FRDs are currently available in production quantities, priced at $5.14/unit (samples, excluding tax).
High-SOA MOSFET is Optimized for 12-V Hot Swap Applications
Alpha & Omega Semiconductor recently released the AONS30300, a 30-V MOSFET with low on-resistance. The AONS30300’s high safe operating area (SOA) suits it for demanding applications, such as hot swap and eFuses, requiring a MOSFET that's robust enough to manage high inrush currents.
The MOSFET offers high SOA robustness under 10 VDS with 10-ms pulse width and an SOA limit of ~48 V. It comes in a compact DFN 5x6 package and has a maximum RDS(on) of 0.58 mΩ at an applied gate-source voltage equal to 10 VGS. In addition, the AONS30300 is rated at Tj = 175°C.
The AONS30300 is immediately available in production quantities with a lead time of 16 weeks. The unit price starts at $2.055 in 1,000-unit quantities. For additional details, click here.
PMIC for IT Devices Equipped with OLED Screens
Magnachip Semiconductor launched its first power-management integrated circuit (PMIC) for IT devices with OLED screens. Based on the company’s integrated power IC technology, this newly designed PMIC communicates with a system by using an inter-integrated circuit (I2C). Therefore, it can control functions such as output-voltage control, ON/OFF block, output-voltage sequence management, protection circuit fault flag, and switching frequency transition—all of which offer seamless connectivity and high performance.
The PMIC’s fast transient response supports a variable refresh rate. This allows a screen to adjust how often it refreshes the image to match the frame rate without user input. As a result, it greatly reduces power consumption and enables a smooth and comfortable viewing experience for games and high-quality videos at refresh rates of 60 ~ 240 Hz.
The device integrates a standalone boost regulator dedicated to powering the application's source and gate drivers, a low-dropout (LDO) regulator, two voltage-reference operational amplifiers, three negative output LDO regulators, three high-current buck regulators driven by a common timing controller, and two operational amplifiers for the gamma buffer. There’s also protection against overvoltage, output short circuits, overcurrent, and low supply voltage, plus a thermal shutdown feature and an output clamping circuit.
For more information, visit www.magnachip.com.
Watch the Maiden Flight of World's First Practical Electric Airliner
After several setbacks and design revisions, a prototype of what's anticipated to be the first commercial electric airliner completed its successful maiden flight at Washington State's Moses Lake Public Airport. With an anticipated price tag of roughly $4 million, the Eviation Alice aircraft features all-composite construction and can carry a two-person crew and up to nine passengers, or 1,100 kg (2,500 lb.) of cargo, while cruising at 407 km/h (253 mph).
The Alice is driven by pair of 850-hp (630 kW) Magni650 electric motor/propeller modules mounted on the aft fuselage. At present, its power source is an 820-kWh lithium-ion battery pack weighing 3,720 kg (8,200 lb.), or roughly 60% of the aircraft's takeoff weight.
Although it had been expected to give the plane an operating range of 440 nautical miles (500 statute miles), the rating was recently reduced to a more conservative 463 km (288 mi/250 nmi). It's expected, however, that advances in storage technology will increase that range over the next few years.
Even with its more constrained performance, the plane is still expected to have operating costs of around $200 per hour (including electricity, maintenance, and battery depreciation), roughly a third of the $600-$900/hr for a comparable twin-turboprop.
As might be expected with such a revolutionary aircraft, the Alice has had several other problems that required significant design revisions and thus reduced its anticipated performance and delayed production. Despite these issues, the company's diligence, sound engineering, and transparency has enabled it to maintain credibility with its customers.
So, even though these issues have delayed delivery of the first aircraft to its alpha customer, Cape Air, until 2027, the regional airline is still firm in its commitment to purchase a total of 92 units. Meanwhile, orders from commercial carriers Deutsche Poste, DHL, and GlobalX Airlines have added another 125+ planes to Eviation's order book.
Additional information about the Alice, and its maiden flight, can be found in its Wikipedia entry and an excellent article by Tina Casey, published September 29, 2022 in CleanTechnica.
Read more articles in the This Week in PowerBites Library Series.