What you’ll learn:
- What is time-sensitive networking and how does it enable time synchronization and traffic shaping?
- How semiconductor producers can modernize their plants with TSN.
- How enablement of new functionality offers a competitive advantage in semiconductor manufacturing.
The production of semiconductors is vital to nearly all modern technologies, helping to drive key breakthroughs in the digitalization of industries and in our daily lives. To help manufacturers deliver high-quality products and ultimately grow under these favorable circumstances, vendors of industrial automation devices should offer cutting-edge technologies such as time-sensitive networking (TSN).
TSN is key to helping companies future-proof their operations by maximizing throughput, productivity, precision, and accuracy. It’s the enabling technology for an industry that needs guaranteed data reliability, integrity, and high performance.
The U.S. is the founder and a global leader in semiconductor R&D, chip design, fabless firms, as well as integrated device and microprocessor manufacturing, with American companies having a combined share of almost 50% of total global semiconductor sales.1 These businesses also are among the most automated, with the sector even surpassing automotive as the largest customer of industrial robots, with approximately 109,000 new units purchased globally in 2020 alone.2
Device vendors serving this sector can extend their current product offerings and take advantage of cutting-edge new technology to drive their customers’ success even further while growing their market share. It’s crucial, in this high-tech sector, for companies to offer advanced, highly competitive solutions that can address the semiconductor industry’s current as well as future challenges and needs.
Data Transparency is a Must for Continuous Improvement
Fabs and other sector-specific manufacturing facilities have a track record of pushing the performance boundaries of automation and smart manufacturing when it comes to semiconductor production. With every technological step forward, they enhance their competitive advantage.
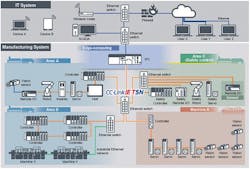
New systems are taking giant steps forward in functionality and performance. System solutions can independently run entire processes, self-optimize their performance, and adapt to varying conditions in real-time (Fig. 1).
Therefore, the first aspect that vendors should deliver with any automation technology destined for the semiconductor industry is maximized performance. This requires access to new levels of process information for both control optimization and process analysis.
Producers of chips and other electronic equipment need to ensure maximum precision and accuracy, operating under stringent and often isolated environmental conditions, to deliver high-quality products. Effective track and trace systems that can monitor the movement of resources and goods across factories as well as the entire supply chain also are needed.
To achieve those goals, it’s crucial to set up a network that, in addition to high speed and deterministic performance capabilities, can support higher enterprise-level systems for robust material tracking and tracing throughout the entire production line. Ultimately, what semiconductor manufacturers require is a network technology to enable the highly effective convergence between the operational technology (OT) and information technology (IT) domains.
Ethernet with TSN Becomes a Game-Changing Market Backbone
TSN is ideal to address these needs. The technology was developed to enhance industrial Ethernet so that it could merge disparate types of data traffic. In effect, thanks to TSN functions, it’s possible to support proprietary automation protocols along with Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) communications.
More precisely, by providing guaranteed data transport with bounded low latencies, networks based on TSN are able to transfer best-effort traffic and mission-critical data in a timely manner.
TSN technology delivers these benefits by enabling advanced time synchronization, traffic shaping, and scheduling methods for traffic prioritization, as set out in the IEEE 802.1 Ethernet standards. In particular, the new clock synchronization can support high-speed, extremely accurate and deterministic operations on the shop floor. This is especially important in motion-control applications that are so prevalent in fab applications.
At the same time, traffic prioritization enables the network to feed different systems with either real-time traffic or best effort traffic. New TSN-based Ethernet switches are all that’s needed for the integration and isolation of high-performance traffic in the enterprise.
Given these key benefits, it becomes clear how applying TSN to automation products can drive up the competitiveness of users as well as developers. More precisely, vendors offering TSN-enabled solutions are able to meet current and future market needs while advancing the performance of their devices.
Standard Industrial Protocols with TSN Support Future-Oriented Devices for Fabs
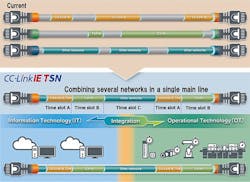
TSN-based Ethernet network technology is crucial to helping vendors deliver truly future-oriented solutions. When vendors opt to use TSN in their products, they can offer TSN functions and enable new levels of performance with their customers. One example of a TSN-ready protocol is CC-Link IE TSN (Fig. 2).
This is the first open industrial Ethernet that combines gigabit bandwidth and TSN. As a result, in addition to traffic synchronization and scheduling, the technology supports today’s Ethernet speeds such as 1-Gb/s transmission rates. This is key to facilitating the prompt, simultaneous transfer of large volumes of IT and OT data from different assets.
CC-Link IE TSN also was designed to provide a broad development ecosystem. Thus, vendors can leverage the tools that are best suited to address their specific needs, in terms of end-product performance as well as time, resources, and investment. Thanks to these features, automation specialists that leverage CC-Link IE TSN can maximize the opportunities available in the semiconductor sectors, helping to drive the industry forward.
Read more articles in the TechXchange: Time for Time-Sensitive Networking.
References
1. Semiconductor Industry Association (SIA) (2021), “2021 State of the U.S. Semiconductor Industry.”
2. International Federation of Robotics (2021), “Executive Summary World Robotics 2021 Industrial Robots.”